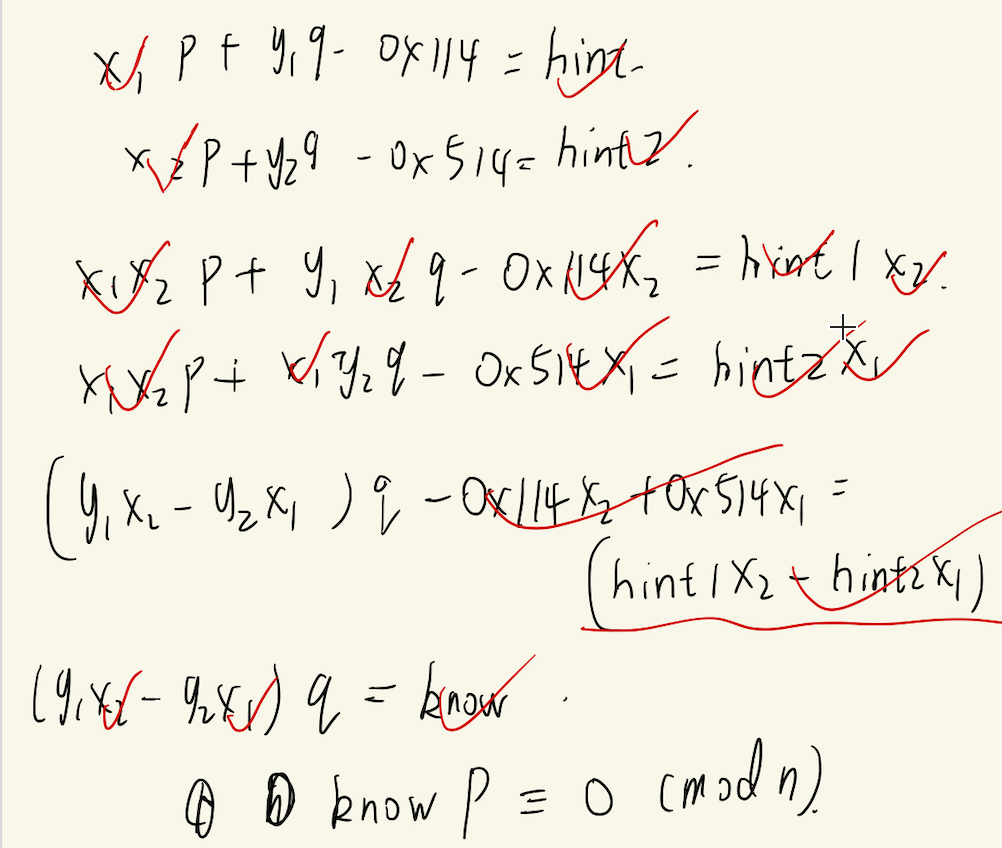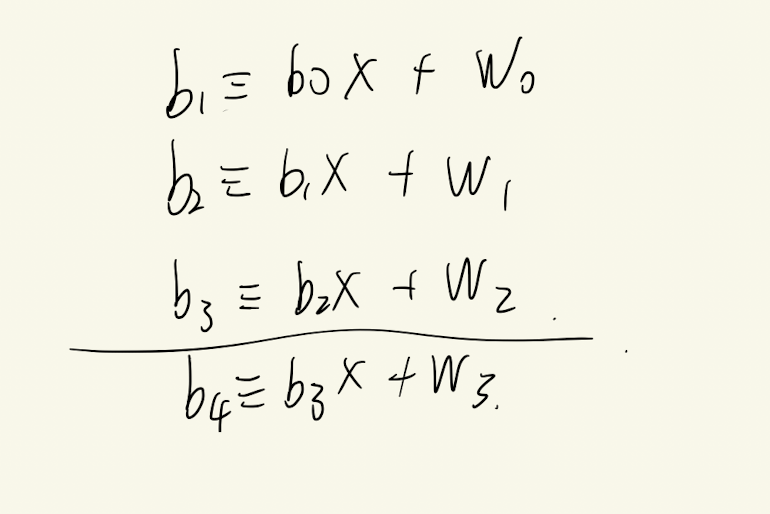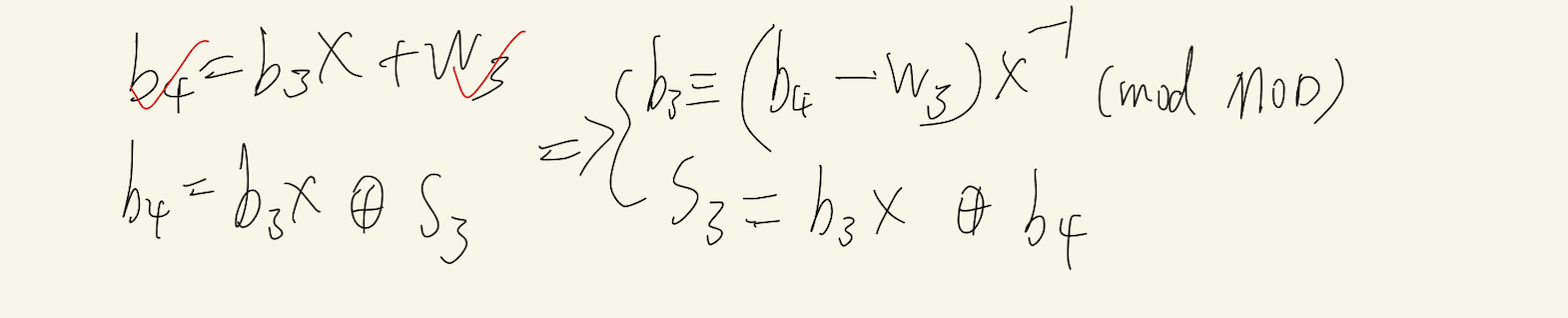rasnd 加密代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, bytes_to_longfrom random import randintimport osFLAG = os.getenv("FLAG" ).encode() flag1 = FLAG[:15 ] flag2 = FLAG[15 :] def crypto1 (): p = getPrime(1024 ) q = getPrime(1024 ) n = p * q e = 0x10001 x1=randint(0 ,2 **11 ) y1=randint(0 ,2 **114 ) x2=randint(0 ,2 **11 ) y2=randint(0 ,2 **514 ) hint1=x1*p+y1*q-0x114 hint2=x2*p+y2*q-0x514 c = pow (bytes_to_long(flag1), e, n) print (n) print (c) print (hint1) print (hint2) def crypto2 (): p = getPrime(1024 ) q = getPrime(1024 ) n = p * q e = 0x10001 hint = pow (514 *p - 114 *q, n - p - q, n) c = pow (bytes_to_long(flag2),e,n) print (n) print (c) print (hint) print ("==================================================================" )crypto1() print ("==================================================================" )crypto2() print ("==================================================================" )
分为两层加密,第一层的话,根据两个hint的等式,直接消掉一个p或者q就行了,然后我们可以得到如下的等式
能满足$$know * p \equiv 0\ (mod\ n)$$,显然就是know和q有倍数关系,所以这边我们直接gcd找他们的因子就可以了
其实到这边得到这个等式之后,有挺多种方法可以做的,除了直接gcd,用solve_mod函数来做也是可以,但是因为这个在爆破,用solve_mod函数太慢了,roots应该也是一样的
当然也有使用费马小定理之后,去计算gcd(pow(2, know, n),n),但是这样实测也非常慢,应该是涉及了幂运算,导致爆破的速度也不理想
exp1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes, inverse, isPrimefrom gmpy2 import iroot, gcdfrom tqdm import trangen1 = 17310686908778728745449354559802941946997896756243856912832576760675562312077799396599231948126385952057312169901033809840639023433489015009822009587919976821459705568133889486358608412949817482914129347583368378773163903299203660972995618294109645144315334549701096983597019368003407750914501919000206577708655243967346282848018490107046949100610467865379900940374382317941626281607014987898420673393221076557550350714383448163376148090492425725769527732209270580359317981591251860111578196496836532090641023922542177760203697279375290470122370953265605033699999237696530837166987965402030511008570227499053858415589 c1 = 16801136688776848905189583066124184181605235613468826025167164990737203785577153779968144287425030876115693615695973552178669507372756662517872836873532372873104381298512676540506180939064702446251055916192839182254160651955152472382129412375165846355186810314277540458462737775658540820351366159791897062706319738582175663161673641264485895479047085644955134173053399210772453274437437650558491343071054681468917598948947849339755507701652954057387144107636550466906541207089179622538211596281963615007936184150772982401572039877033189118382151964903168743863988864938773395153618109854626801894827551132349825934048 hint1 = 2477996433220738043622133780345574935136056477634270387691415040860651816313698350481105379393606643792493933030252187985540480193826844575786917504563212615591947336827131036061865020453648292790252977476741824597421573128221147373241709525069458483831823196234210561124714908044630499381066408414577413328176041616410349558032896455987496268 hint2 = 3137475932416527139286634960823544631965548664103993358517488315320409377390611754271852553601794986938848132860809744270918113110601431725955064776295841568126005906161924413611266529442263492723531092767851370933688086426874790580454813935496647372763389302737474208961448740153404073860193314600613913409394507452478113751942840536864875073701069386553808604224372149844554572364248242010448859521005078087076922560295908636574339399105701048880829362161183847 for x1 in trange(1 , 2 ^ 11 ): for x2 in range (1 , 2 ^ 11 ): know = (hint1 * x2 - hint2 * x1) + 0x114 * x2 - 0x514 * x1 if gcd(know, n1) != 1 : q = int (gcd(know, n1)) % n1 e = 65537 p = n1 // q phi = (p - 1 ) * (q - 1 ) d1 = inverse(e, phi) print (long_to_bytes(int (pow (c1, d1, n1))))
对于第二层加密的话,直接解一个二元一次方程就可以了(利用到欧拉定理)
exp2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes, inverse, isPrimefrom gmpy2 import iroot, gcdn2 = 17852379230831263077492443645517524782877703753693408080027712402383930619845734003191922568470099156757227518418841934348678705692807610487502903475066212024016026772695709874654434071759886847144987627824309040318953055819128137532342600218127375922396169571417060075251837131440789009020281380594551495034506456568639317302650233612183779579388683143456858997880819263732249622210137939698730563046214821230634103313220529125021058999182014757244533018469768194481448634804668491520969148003100428422906592828506579812678209726723490155171972379460695868749876659068978259534378528342458577249471485939878071066781 c2 =6457124454630977279083318517136056048994981657102713798861789132946960924788454240045022016749103040038582397266779376922458258879511238711863439172573992672269944281196228832026042788514833807851569807895848773612307107332200937270911202540034907126676830220795450294815846685344274249632796298518652045091113814607892734554835452797267462127322858988899801977668506314249485852001119727739173290541474856419753187538834950880723377243590331445468284278069552329365325402280743189571012755120987340894641050440177292175527281744110219913880353494263914566043077027966527392323264935214909513300432715625591998932278 hint2 = 7022928469215188794896159363114216103264137878166634936619665468565860894410179602925380205654804344175484822946774664548850198574273507877356676945333658983326465614140366844687501782669688509290255495687946212664207595107103278265123751844101029087286192458571447776880684457682304092209759498024170110943489459735345987232782942337036666190988352534111964443352600615267949091000136931756580923914824359453466918676964147705663433852995198096337163404473487073140676231970342261180171821824455950519091774102747410457593553416780633424458115273755507656388667082208435890865202586317510023135252865190973648070447 p = (inverse(hint2, n2) + iroot(int (inverse(hint2, n2) ^ 2 + 4 * 514 * 114 * n2), 2 )[0 ]) // (2 * 514 ) q = n2 // p phi = (p - 1 ) * (q - 1 ) e = 0x10001 d2 = inverse(e, phi) print (long_to_bytes(int (pow (c2, d2, n2))))
fffffhash 今年的CISCN就有格做法的了
加密代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import osfrom Crypto.Util.number import *def giaogiao (hex_string ): base_num = 0x6c62272e07bb014262b821756295c58d x = 0x0000000001000000000000000000013b MOD = 2 **128 for i in hex_string: base_num = (base_num * x) & (MOD - 1 ) base_num ^= i return base_num giao=201431453607244229943761366749810895688 print ("1geiwoligiaogiao" )hex_string = int (input (),16 ) s = long_to_bytes(hex_string) if giaogiao(s) == giao: print (os.getenv('FLAG' )) else : print ("error" )
思路很简单,去年是用中间相遇攻击打的,不过那个极限应该在7位左右,这次位数都不知道了,很明显用格打才行,然后爆破一手位数就可以了
以s的长度是4为例(就是把异或看做是加法,用w来代表所对应的误差
造个得先拿等式,本地测试一下,构造出来的等式应该是类似这样的
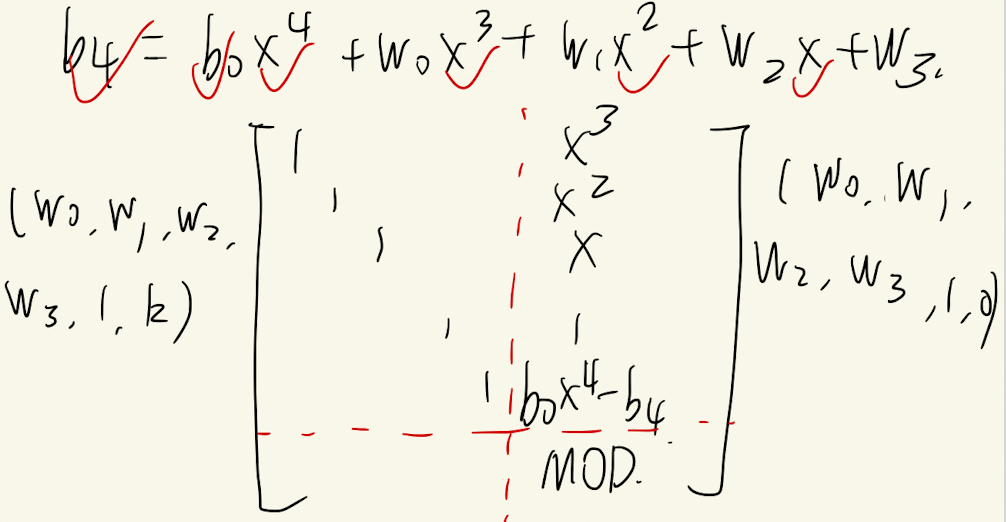
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 b0, b1, b2, w0, w1, w2, w3, x = var('b0, b1, b2, w0, w1, w2, w3, x' .replace(',' , '' )) bb3 = b2 * x + w2 bb2 = b1 * x + w1 bb1 = b0 * x + w0 b4 = b3 * x + w3 b4.subs(b3 = bb3).subs(b2 = bb2).subs(b1 = bb1).expand()
1 b0*x^4 + w0*x^3 + w1*x^2 + w2*x + w3
根据等式我们很明显可以构造出如下的格
然后规约得到的w0,w1,w2,w3就是误差,满足
由此类推即可得到s3,s2,s1,s0
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes, inverse, isPrimefrom gmpy2 import iroot, gcdfrom tqdm import trangeimport itertoolsimport sysb0 = 0x6c62272e07bb014262b821756295c58d x = 0x0000000001000000000000000000013b giao=201431453607244229943761366749810895688 MOD = 2 **128 for num in trange(1 , 50 ): B = [giao] tmp, S = [], [] for i in range (num - 1 , -1 , -1 ): tmp.append(x ^ i) tmp.append(b0 * x ^ num - giao) L = block_matrix([[identity_matrix(num + 1 ), Matrix(ZZ, num + 1 , 1 , tmp)], [Matrix(ZZ, 1 , num + 1 ), MOD]]) Q = diagonal_matrix(ZZ, [1 ] * num + [128 ] + [2 ^ 128 ]) L = L * Q res = L.BKZ() for j in res: if abs (j[-2 ]) == 128 and j[-1 ] == 0 : if j[-2 ] == 128 : my = j[:-2 :] for w in range (len (my) - 1 , -1 , -1 ): tmp_b = (B[-1 ] - my[w]) * inverse(x, MOD) % MOD B.append(tmp_b) S.append(((tmp_b * x) ^^ B[-2 ]) % MOD) if all (0 <= w <= 256 for w in S): print (bytes (S[::-1 ]).hex ()) elif j[-2 ] == -128 : my = [-lll for lll in j[:-2 :]] for w in range (len (my) - 1 , -1 , -1 ): tmp_b = (B[-1 ] - my[w]) * inverse(x, MOD) % MOD B.append(tmp_b) S.append(((tmp_b * x) ^^ B[-2 ]) % MOD) if all (0 <= w <= 256 for w in S): print (bytes (S[::-1 ]).hex ())
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 020101081b04390001051a020a3d0f0f 1df2006d2e3362153d001f53102a7c2a0a591516 f7d210031a28123358f217313d0f1d070d043a2215 df3beb01fd05000d1f09147c051c6f0000090aed273d00 070e092f101f387d22071b040308766d3901030d3f091d03 fc1d0c00030202030d020b0c06191e3908121a03fb03181c041e090d0d 010f0500020704011603017f0c191e02080b0d023c0d3f0a18130b060204 f406021c0405040937031f0e7f0d1a0f020e0b0400070104010e05070e020502 fffe020f06030a05020f023a010f3c3b010f020a04067d0d0f021f040c0202070002 01030104001efb070e03050f043e027c0f1c0b3d02011b02017600020400050607040f 030406041e043d1d05011b060c07070a1f060d3c070e000f060c0f130e043c0102020d0f 01070107000d0201040507040e06010d0b070303001c0200000301010f041c0e0a3f3c02060202 030603070004040a003d030203000207011e0704fd00021c0600060005010302060707070101040d fe0703010507021f01020d0401030203001d070e0f060f3d000f0e0103061b031f07010203013d06020e 000d0e000e0d0c0e1d01030e013e037d061e02060e02000102020207033c03001d010703050404fc073e000f 01001f000d0700003c0000001f0f07011e060101030101000602010106071c0305000e010dfc040d0100060401 010d030301030e1c06050b0700001f063f0300021e02000e0f06010100010300020200050f010207040202030f00 ff010701020003010302070005010e000102000c0a030500030000020103010007020006050a0005011c0505010c040003
其中070e092f101f387d22071b040308766d3901030d3f091d03为我们所要求的
2025-2-24
你发现这里终于更新了!(๑•̀ω•́)ノ最近课比较少,忽然想到这题当时没做出来,因为网上似乎没有关于这题的wp,反正我是找不到,所以花了半天的时间复现一下。
lwewl 加密代码(简单加了点注释):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 from Crypto.Util.number import *from random import randintfrom secret import flagassert flag.startswith(b'flag{' ) and flag.endswith(b'}' )flag = flag[5 :-1 ] flag1 = flag[:len (flag)//2 ] flag2 = flag[len (flag)//2 :] class LWE : def __init__ (self, lwe_dim, lwe_num_samples, lwe_plaintext_modulus, lwe_ciphertext_modulus, rlwe_dim, rlwe_modulus ): self .lwe_dim = lwe_dim self .lwe_num_samples = lwe_num_samples self .lwe_plaintext_modulus = lwe_plaintext_modulus self .lwe_ciphertext_modulus = lwe_ciphertext_modulus self .lwe_secret_key = self .distribution(0 , self .lwe_ciphertext_modulus - 1 , self .lwe_dim) self .rlwe_dim = rlwe_dim self .rlwe_modulus = rlwe_modulus def distribution (self, lbound, rbound, dim ): return [randint(lbound, rbound) for _ in range (dim)] def lwe_encrypt (self, message ): a = self .distribution(0 , lwe_ciphertext_modulus - 1 , self .lwe_dim) e = self .distribution(-15 , 15 , 1 )[0 ] return a, sum ([a[i] * self .lwe_secret_key[i] for i in range (self .lwe_dim)]) + message + e * lwe_plaintext_modulus def lwe_keygen (self ): A = [] B = [] for _ in range (self .lwe_num_samples): sample = self .lwe_encrypt(0 ) A.append(sample[0 ]) B.append(sample[1 ]) return A, B def encrypt (self, message, lwe_pubkey1, lwe_pubkey2 ): const = vector(ZZ, self .distribution(-1 , 1 , self .lwe_num_samples)) e = self .distribution(-15 , 15 , 1 )[0 ] return const * matrix(GF(lwe_ciphertext_modulus), lwe_pubkey1), const * vector(GF(lwe_ciphertext_modulus), lwe_pubkey2) + message + e * lwe_plaintext_modulus def rlwe_sample (self, flag ): P.<x> = PolynomialRing(Zmod(self .rlwe_modulus)) while True : monomials = [x^i for i in range (self .rlwe_dim + 1 )] c = self .distribution(0 , self .rlwe_modulus - 1 , self .rlwe_dim) + [1 ] f = sum ([c[i] * monomials[i] for i in range (self .rlwe_dim + 1 )]) PR = P.quo(f) if f.is_irreducible(): break a = self .distribution(0 , self .rlwe_modulus - 1 , self .rlwe_dim) e = self .distribution(-5 , 5 , self .rlwe_dim) s = [flag[i] for i in range (len (flag))] b = PR(a) * PR(s) + PR(e) return a, b, f, self .rlwe_modulus lwe_dimension = 2 **9 lwe_num_samples = 2 **9 + 2 **6 + 2 **5 + 2 **2 lwe_plaintext_modulus = next_prime(256 ) lwe_ciphertext_modulus = next_prime(1048576 ) rlwe_dim = 64 rlwe_modulus = getPrime(128 ) lwe = LWE(lwe_dimension, lwe_num_samples, lwe_plaintext_modulus, lwe_ciphertext_modulus, rlwe_dim, rlwe_modulus) lwe_pubkey1, lwe_pubkey2 = lwe.lwe_keygen() lwe_public_key = [lwe_pubkey1, lwe_pubkey2] lwe_cipher1 = [] lwe_cipher2 = [] for flag_char in flag1: tmp1, tmp2 = lwe.encrypt(flag_char, lwe_pubkey1, lwe_pubkey2) lwe_cipher1.append(tmp1) lwe_cipher2.append(tmp2) lwe_ciphertext = [lwe_cipher1, lwe_cipher2] save(lwe_public_key, "lwe_public_key" ) save(lwe_ciphertext, "lwe_ciphertext" ) rlwe_ciphertext = lwe.rlwe_sample(flag2) save(rlwe_ciphertext, "rlwe_ciphertext" )
确实是有难度,读题都要读好一会,只能说要想在规定时间内做出来,除非做过原题,不然真不太可能
题目分为两部分加密,第一部分是lwe加密(其实也有点像dlwe),第二部分是一个rlwe加密
我们先看lwe_encrypt 函数和lwe_keygen 函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def lwe_encrypt (self, message ): a = self .distribution(0 , lwe_ciphertext_modulus - 1 , self .lwe_dim) e = self .distribution(-15 , 15 , 1 )[0 ] return a, sum ([a[i] * self .lwe_secret_key[i] for i in range (self .lwe_dim)]) + message + e * lwe_plaintext_modulus def lwe_keygen (self ): A = [] B = [] for _ in range (self .lwe_num_samples): sample = self .lwe_encrypt(0 ) A.append(sample[0 ]) B.append(sample[1 ]) return A, B
我们知道lwe_pubkey1 是一个612 × 512 612\times 512 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 A 612 × 512 A_{612 \times 512} A 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 ,lwe_pubkey2 是一个612 × 1 612\times1 6 1 2 × 1 B 612 × 1 B_{612\times 1} B 6 1 2 × 1
A 612 × 512 ⋅ s 512 × 1 + 257 ⋅ E 612 × 1 = B 612 × 1 A_{612 \times 512}\cdot s_{512\times 1} + 257\cdot E_{612\times 1} =B_{612\times 1}
A 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 ⋅ s 5 1 2 × 1 + 2 5 7 ⋅ E 6 1 2 × 1 = B 6 1 2 × 1
然后这边的A 612 × 512 A_{612 \times 512} A 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 B 612 × 1 B_{612\times 1} B 6 1 2 × 1 s 512 × 1 s_{512\times 1} s 5 1 2 × 1 e 612 × 1 e_{612\times 1} e 6 1 2 × 1
我们先继续看encrypt 函数,是加密flag1 的
1 2 3 4 def encrypt (self, message, lwe_pubkey1, lwe_pubkey2 ): const = vector(ZZ, self .distribution(-1 , 1 , self .lwe_num_samples)) e = self .distribution(-15 , 15 , 1 )[0 ] return const * matrix(GF(lwe_ciphertext_modulus), lwe_pubkey1), const * vector(GF(lwe_ciphertext_modulus), lwe_pubkey2) + message + e * lwe_plaintext_modulus
这边的const,是一个1 × 612 1\times612 1 × 6 1 2 c 1 × 612 c_{1\times612} c 1 × 6 1 2
c 1 × 612 ⋅ A 612 × 512 = l w e _ c i p h e r 1 c 1 × 612 ⋅ B 612 × 1 + m 0 + 257 ⋅ e 0 = l w e _ c i p h e r 2 \begin{array}{l}
c_{1\times612}\cdot A_{612 \times 512}=lwe\_cipher1\\
c_{1\times612}\cdot B_{612 \times 1} + m_0 + 257 \cdot e_0=lwe\_cipher2
\end{array}
c 1 × 6 1 2 ⋅ A 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 = l w e _ c i p h e r 1 c 1 × 6 1 2 ⋅ B 6 1 2 × 1 + m 0 + 2 5 7 ⋅ e 0 = l w e _ c i p h e r 2
lwe_cipher1 和lwe_cipher2 我们都是知道的,然后A 612 × 512 A_{612 \times 512} A 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 c 1 × 612 c_{1\times612} c 1 × 6 1 2 A 612 × 512 A_{612 \times 512} A 6 1 2 × 5 1 2 c 0 c_0 c 0
这边简单介绍一下知识点
左核空间
对于矩阵A A A Y A = 0 YA = 0 Y A = 0
左核空间的维度为p − rank ( A ) p - \text{rank}(A) p − rank ( A )
左核空间的一组基可以表示为 K 1 , K 2 , … , K k K_1, K_2, \ldots, K_k K 1 , K 2 , … , K k k = p − rank ( A ) k = p - \text{rank}(A) k = p − rank ( A )
通解的表示
通常,方程 $ XA = B $ 的通解可以表示为:
X = X 0 + t 1 K 1 + t 2 K 2 + ⋯ + t k K k X = X_0 + t_1K_1 + t_2K_2 + \cdots + t_kK_k
X = X 0 + t 1 K 1 + t 2 K 2 + ⋯ + t k K k
其中:
X 0 X_0 X 0 K 1 , K 2 , … , K k K_1, K_2, \ldots, K_k K 1 , K 2 , … , K k t 1 , t 2 , … , t k t_1, t_2, \ldots, t_k t 1 , t 2 , … , t k
对于这题,我们的通解就可以表示为
c 1 × 612 = c 0 + t 1 K 1 + t 2 K 2 + ⋯ + t k K k c_{1\times612} = c_0 + t_1K_1 + t_2K_2 + \cdots + t_kK_k
c 1 × 6 1 2 = c 0 + t 1 K 1 + t 2 K 2 + ⋯ + t k K k
也就是对
c 1 × 612 = c 0 + t 1 × 100 ⋅ K 100 × 612 c_{1\times612} = c_0 + t_{1\times 100}\cdot K_{100\times 612}
c 1 × 6 1 2 = c 0 + t 1 × 1 0 0 ⋅ K 1 0 0 × 6 1 2
这边的t 1 × 100 t_{1\times 100} t 1 × 1 0 0 ( t 1 , t 2 , … , t 100 ) ( t_1,\ t_2,\ \ldots,\ t_{100} ) ( t 1 , t 2 , … , t 1 0 0 ) K 100 × 612 K_{100\times 612} K 1 0 0 × 6 1 2
那么对于这样的,显然我们可以构造如下的格来(lwe_ciphertext_modulus设为q)
L = [ K 100 × 612 c 0 q 612 × 612 ] L=\begin{bmatrix}
K_{100\times 612}\\
c_0\\
q_{612\times 612}
\end{bmatrix}
L = ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ K 1 0 0 × 6 1 2 c 0 q 6 1 2 × 6 1 2 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
该格满足
( t 1 , t 2 , … , t 100 , 1 , k 1 , k 2 , … , k 612 ) [ K 100 × 612 c 0 q 612 × 612 ] = c 1 × 612 \begin{array}{l}
( t_1,\ t_2,\ \ldots,\ t_{100},\ 1, k_1,\ k_2,\ \ldots,\ k_{612})
\begin{bmatrix}
K_{100\times 612}\\
c_0\\
q_{612\times 612}
\end{bmatrix}
= c_{1\times612}
\end{array}
( t 1 , t 2 , … , t 1 0 0 , 1 , k 1 , k 2 , … , k 6 1 2 ) ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ K 1 0 0 × 6 1 2 c 0 q 6 1 2 × 6 1 2 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤ = c 1 × 6 1 2
但是这个格的维度是713 × 612 713\times 612 7 1 3 × 6 1 2 两种做法
第一种 方法就是利用规约的结果和L L L L L L
第二种 方法就是对格再做一下改进,构造如下的格(也就是再加一列)
L = [ K 100 × 612 0 100 × 1 c 0 1 q 612 × 612 0 612 × 1 ] L=\begin{bmatrix}
K_{100\times 612}&0_{100\times 1}\\
c_0&1\\
q_{612\times 612}&0_{612\times 1}
\end{bmatrix}
L = ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ K 1 0 0 × 6 1 2 c 0 q 6 1 2 × 6 1 2 0 1 0 0 × 1 1 0 6 1 2 × 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤
该格满足
( t 1 , t 2 , … , t 100 , 1 , k 1 , k 2 , … , k 612 ) [ K 100 × 612 0 100 × 1 c 0 1 q 612 × 612 0 612 × 1 ] = ( c 1 × 612 , 1 ) \begin{array}{l}
( t_1,\ t_2,\ \ldots,\ t_{100},\ 1, k_1,\ k_2,\ \ldots,\ k_{612})
\begin{bmatrix}
K_{100\times 612}&0_{100\times 1}\\
c_0&1\\
q_{612\times 612}&0_{612\times 1}
\end{bmatrix}
= (c_{1\times612},\ 1)
\end{array}
( t 1 , t 2 , … , t 1 0 0 , 1 , k 1 , k 2 , … , k 6 1 2 ) ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ K 1 0 0 × 6 1 2 c 0 q 6 1 2 × 6 1 2 0 1 0 0 × 1 1 0 6 1 2 × 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤ = ( c 1 × 6 1 2 , 1 )
这时候我们只要判断规约结果的第613元素的正负就可以判断规约结果的正负了
得到完整的c 1 × 612 c_{1\times612} c 1 × 6 1 2
m 0 = l w e _ c i p h e r 2 − c 1 × 612 ⋅ B 612 × 1 ( m o d 257 ) m_0 =lwe\_cipher2 - c_{1\times612}\cdot B_{612 \times 1}\ (mod\ 257)
m 0 = l w e _ c i p h e r 2 − c 1 × 6 1 2 ⋅ B 6 1 2 × 1 ( m o d 2 5 7 )
这边同时还要注意,c 1 × 612 ⋅ B 612 × 1 c_{1\times612}\cdot B_{612 \times 1} c 1 × 6 1 2 ⋅ B 6 1 2 × 1 F q F_q F q l w e _ c i p h e r 2 − c 1 × 612 ⋅ B 612 × 1 lwe\_cipher2 - c_{1\times612}\cdot B_{612 \times 1} l w e _ c i p h e r 2 − c 1 × 6 1 2 ⋅ B 6 1 2 × 1 q 2 \frac{q}{2} 2 q m m m F q F_q F q q 2 \frac{q}{2} 2 q
总的来说思路能想到这已经是不容易了
因为是不断随机选择列向量进行规约的,那么肯定是要多线程进行了,同时还要处理随机选择的逻辑,这exp指定是要憋很久了⁄(⁄ ⁄•⁄ω⁄•⁄ ⁄)⁄
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 from multiprocessing import Poolfrom random import shufflefrom tqdm import trangedef attack (range_ ): q = next_prime(1048576 ) lwe_pubkey1, lwe_pubkey2 = load('lwe_public_key.sobj' ) lwe_cipher1, lwe_cipher2 = load('lwe_ciphertext.sobj' ) A = matrix(GF(q), 612 , 512 , lwe_pubkey1) B = matrix(GF(q), 612 , 1 , lwe_pubkey2) K = A.left_kernel().basis_matrix() def solve_c (c0, cols ): ALL = list (range (612 )) shuffle(ALL) sols = [] for i in range (0 , 612 , cols): sel = ALL[i:i + cols] KK = matrix(ZZ, [K.column(j) for j in sel]).T L = KK.stack(matrix(ZZ, [c0[0 ][j] for j in sel])).stack(identity_matrix(cols) * q).augment(matrix(ZZ, 254 , 1 , [0 ] * 100 + [1 ] + [0 ] * cols)) res = L.LLL() for row in res: if all (-1 <=j <= 1 for j in row): if row[-1 ] == 1 : sols.append((sel, row[:-1 :])) elif row[-1 ] == -1 : sols.append((sel, -row[:-1 :])) return sols tmp_flag = '' low, high = range_[0 ], range_[1 ] for ii in trange(low, high): tmp1, tmp2 = lwe_cipher1[ii], lwe_cipher2[ii] c = vector([0 ] * 612 ) c0 = A.solve_left(matrix(GF(q), 1 , 512 , tmp1)).change_ring(ZZ) sols = solve_c(c0, 153 ) for sel, row in sols: for idx, val in zip (sel, row): c[idx] = val tmp = ZZ(tmp2) - ZZ((c * B)[0 ]) if tmp >= q // 2 : tmp -= q m = tmp % 257 e = (tmp - m) // 257 assert -15 <= e <= 15 tmp_flag += chr (m) return tmp_flag if __name__ == "__main__" : flag1 = '' ranges = [(i, i + 3 ) for i in range (0 , 18 , 3 )] with Pool(6 ) as pool: tmp_flag = pool.imap(attack, ranges) flag1 = '' .join(tmp_flag) print (flag1)
没想到半小时就写完了,其实也不没有那么难写(´◉‿◉`),开6线程我的M1大概4分钟能跑完
当然这个代码是可以优化的,比如求核空间,读取数据什么的可以放main函数里面,但是实测这些格外的操作并不需要花多少时间,而且我也不喜欢给函数传递太多变量,看起来很繁琐,所以干脆直接都放一起
这部分比较简单,一眼就能看出怎么造格了,其实难点主要还是第一部分
在Z p [ x ] / ( f ( x ) ) \mathbb{Z}_p[x]/(f(x)) Z p [ x ] / ( f ( x ) ) f ( x ) f(x) f ( x ) x 64 + c 63 ∗ x 63 + ⋯ + c 1 ∗ x + 1 x^{64} + c_{63}*x^{63} + \cdots + c_1*x + 1 x 6 4 + c 6 3 ∗ x 6 3 + ⋯ + c 1 ∗ x + 1
a ∗ s + e = b a * s + e = b
a ∗ s + e = b
e e e e r r o r error e r r o r
a a a b b b p p p rlwe_modulus 为p p p
思路很直接,变形一下,得到
a ∗ s − b = − e a*s-b = -e
a ∗ s − b = − e
我们知道,对于商环下的乘法运算,可以转为矩阵上来运算,具体可以看我西湖论剑那题的做法
1 https://suhanhan-cpu.github.io/2025/02/12/2025-%E8%A5%BF%E6%B9%96%E8%AE%BA%E5%89%91-New-Year-Ring4-wp%E5%A4%8D%E7%8E%B0/
使用如下的一句话代码:
1 mat = Matrix(ZZ, [(mult*x^i % mod).list () for i in range (mod.degree())])
mod为对应的模多项式,本题对应就是14
mult为要转为矩阵的多项式,注意是定义在多项式环下,不是商环
将多项式a a a A A A
S 1 × 64 ⋅ A 64 × 64 − B 1 × 64 = − e 1 × 64 S_{1\times 64}\cdot A_{64\times 64} - B_{1\times 64} = -e_{1\times 64}
S 1 × 6 4 ⋅ A 6 4 × 6 4 − B 1 × 6 4 = − e 1 × 6 4
写到这的时候发现,s(也就是flag2)的长度我们不知道,不过第一部分我们已经求得一半的flag了,看起来应该是uuid4的格式,那么后半部分的flag长度其实也是18(去掉头和尾),如果不知道估计也得多线程爆破了
那么S 1 × 64 S_{1\times 64} S 1 × 6 4
( s 0 , s 1 , s 2 , ⋯ , s 17 , 0 , 0 , … , 0 ⏟ 46 个 ) (s_0,\ s_1,\ s_2, \cdots,\ s_{17},\ \underbrace{0,\ 0,\ \dots,\ 0}_{46\text{个}})
( s 0 , s 1 , s 2 , ⋯ , s 1 7 , 4 6 个 0 , 0 , … , 0 )
注意到S 1 × 64 S_{1\times 64} S 1 × 6 4
显然可以构造如下的格
L = [ A 64 × 64 0 64 × 1 − B 1 × 64 1 p 64 × 64 0 64 × 1 ] + [ I 18 × 18 0 111 × 18 ] L=\begin{bmatrix}
A_{64\times 64} & 0_{64\times 1}\\
-B_{1\times 64} & 1\\
p_{64\times 64} & 0_{64\times 1}&
\end{bmatrix}
+
\begin{bmatrix}
I_{18\times 18}\\
0_{111\times 18}
\end{bmatrix}
L = ⎣ ⎢ ⎡ A 6 4 × 6 4 − B 1 × 6 4 p 6 4 × 6 4 0 6 4 × 1 1 0 6 4 × 1 ⎦ ⎥ ⎤ + [ I 1 8 × 1 8 0 1 1 1 × 1 8 ]
该格满足
( s 0 , s 1 , s 2 , ⋯ , s 17 , 0 , 0 , … , 0 ⏟ 46 个 , 1 , k 0 , k 1 , ⋯ , k 63 ) L = ( e 0 , e 1 , ⋯ , e 63 , 1 , s 0 , s 1 , ⋯ , s 17 ) \begin{array}{l}
(s_0,\ s_1,\ s_2, \cdots,\ s_{17},\ \underbrace{0,\ 0,\ \dots,\ 0}_{46\text{个}},\ 1,\ k_0, k_1,\ \cdots,\ k_{63})
L=(e_0, e_1,\ \cdots,\ e_{63},\ 1,\ s_0, s_1,\ \cdots,\ s_{17})
\end{array}
( s 0 , s 1 , s 2 , ⋯ , s 1 7 , 4 6 个 0 , 0 , … , 0 , 1 , k 0 , k 1 , ⋯ , k 6 3 ) L = ( e 0 , e 1 , ⋯ , e 6 3 , 1 , s 0 , s 1 , ⋯ , s 1 7 )
注意配平即可
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 a, b, f, p = load('rlwe_ciphertext.sobj' ) PR.<x> = PolynomialRing(GF(p)) f = PR(f) A = Matrix(ZZ, [(PR(a)*x^i % f).list () for i in range (64 )]) B = Matrix(ZZ, 1 , 64 , [ZZ(i) for i in b]) LL = block_matrix(ZZ, [[A, Matrix(ZZ, 64 , 1 )], [-B, 1 ], [identity_matrix(64 ) * p, Matrix(ZZ, 64 , 1 )]]) LR = identity_matrix(18 ).stack(Matrix(ZZ, 111 , 18 )) L = LL.augment(LR) for _ in range (L.nrows() - L.ncols()): L = L.augment(vector([0 ] * 129 )) L *= diagonal_matrix(ZZ, [64 ] * 64 + [64 ] + [1 ] * 64 ) L = L.delete_columns(list (range (83 , 129 ))) res = L.LLL() for row in res: if row[64 ] == -64 : row = -row if row[64 ] == 64 : if all (0 < j < 255 for j in row[65 ::]): flag2 = [ZZ(j) for j in row[65 ::]] flag2 = bytes (flag2) if flag2.isascii(): print (flag2) break
当然这边想优化规约速度的话primal attack优化版本,不过这题就完全没有必要了